部落格同步刊登 [IT 鐵人賽] Router 基本入門 Day 9
聊完狀態管理之後,我們來聊一下前端的路由。最近各大家前端工具都有支援前端路由的功能。而 Vue-Router 是官方推出的。功能上都大同小異,你也可以自己做一個(我最喜歡自己做輪子了)。
如果你做好了記得開源出來~
前端做這件事情應該是 Angular 起了一個頭,畢竟身為 Google 的親生兒子,所以很熱門。其實他並不是什麼很新穎的技術,主要是依靠 HTML5 History API 來做操作。在不支援 History API 的瀏覽器當中,大多都是使用 URL hash 的方式來達成。
例如說:
#/hoomepage
#/helloworld
#/uccu
然後 HTML5 History API 出現之後,我們就能直接去操作網址,看起來就比較美觀。這裡有一個大前提,我們需要將 Web Server 把所有的請求,都指向你的 index.html。
而 Vue Router 的使用方式也很簡單,
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import App from '@/App.vue';
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue';
Vue.use(Router)
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/helloworld',
component: HelloWorld,
meta: {},
children: []
}
]
});
new Vue({
router: router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
你在 new Vue 的時候,把 Router 放進去就可以了。
這個路由設定有幾個屬性可以使用:
mode 路由模式,可用數值有:
hash 瀏覽器預設,就是 URL hash 的方式。history 使用 HTML5 History API 的方式。abstract 所有 JavaScript 環境皆可用。如果取不到瀏覽器 API,會強制進入這模式。base 路由的根路徑,預設是使用 / 這個根路徑。routes 是個陣列,裡面包含了你的路由設定。linkActiveClass 設定 全域 的 <router-link> 若路由相符,會加入的 class 名稱。linkExactActiveClass 跟上一個很類似,但你的路由必須要「完全相同」才會加入 class 名稱。scrollBehavior 設定捲軸的屬性,例如你想要「上一頁」回到某個特定位置的時候。parseQuery 解析查詢字串的自定義函式,會覆蓋預設函式。stringifyQuery 反解析查詢字串的自定義函式,會覆蓋預設函式。fallback 僅接受布林值,當你的路由模式不支援 History API 時,會退回去使用 URL hash 的方式,預設為 true。而這個 Router 的內建方法有:
beforeEach 當路由開始進入之前,會執行此函式。函式會回傳三個參數,
to 將要前往的 Route 物件實例。from 來源的 Route 物件實例。next 這形同於回呼函式,你必須要呼叫他 next() 他才會繼續往下做。beforeResolve 當路由內部的所有路由防護規則都被解析之後執行,跟 beforeEach 一樣有三個參數。afterEach 當路由結束操作後,會呼叫此函數。跟 beforeEach 一樣,但是沒有 next() 的回呼函式。push 類似 History API 的 pushState,本身是可以接受 Promise 操作。replace 類似 History API 的 replaceState,本身是可以接受 Promise 操作。go 類似 History API 的 go,傳入的是步驟數字。back 你可以把他想像成,把 go 傳入負值,例如 go(-1)。forward 跟 go 很類似的操作。resolve 取回一個解析過的 URL,他可以返回:
location 回傳 Location 物件實例。route 回傳 Route 物件實例。href 回傳 URL 字串。getMatchedComponents 回傳解析路徑後所符合的 Vue 元件。addRoutes 加入路由,這個路由是陣列格式。onReady 所有的路由以及路由所使用的 Vue 元件都解析完成後,會呼叫此函數。onError 路由以及路由所使用的 Vue 元件解析若有錯誤,會呼叫此函數。我們從比較基礎的部分來講,最主要是 routes 的相關設定,他僅能接受 Route 設定資料物件,這個物件本身包含了以下幾個屬性跟方法:
path 路徑,從 base 開始算。name 這一個路由的名稱,他會在一些路由方法中可以使用。component 這個路由配置的 Vue 元件。components 設置有命名規則的 Vue 元件。redirect 重新導向路徑,可以是字串﹑Location 物件或是函式。props 將路由上面的正規配置當作屬性傳入元件當中,可以是布林值、物件或函式。alias 路由別名,可以是字串或是字串組成的陣列。children 嵌套路由,就是這個路由的兒子(你可以這麼理解沒問題)。meta 可傳入任何值,用於路由本身的資料集。beforeEnter 進入此路由前,會先執行的防禦路由方法函式,自身會帶入 to, from 與 next() 參數。caseSensitive 路由本身是否區身大小寫,僅接受布林值,預設為 false。Path-to-RegExp 可接受 Path-to-RegExp 的設定。我們用文章一開始的例子來擴充解釋:
import Router from 'vue-router'
import NotFound from '@/components/NotFound.vue'
import HelloKittyWithId from '@/components/HelloKittyWithId.vue'
import HelloKittyWithName from '@/components/HelloKittyWithName.vue'
import HelloKitty from '@/components/HelloKitty.vue'
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
import PathRegex from '@/components/PathRegex.vue'
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/helloworld',
name: 'HelloWorld',
component: HelloWorld,
beforeEnter (to, from, next) {
if (from.name === 'HelloKitty') {
next({ to: 'NotFound' })
}
next()
},
meta: {
pageNeedLogin: true,
showFooter: false
},
children: [
{
path: 'dark',
name: 'HelloDarkWorld',
component: HelloDarkWorld
}
]
},
{
path: '/hellokitty',
name: 'HelloKitty',
component: HelloKitty,
children: [
{
path: 'id/:id',
name: 'HelloKittyWithId',
components: {
a: HelloKittyWithId,
b: HelloKittyWithName
},
props: true
}
],
alias: [
'hellokitty-alias',
'hellokitty-ok'
]
},
{
path: '/path-to-regex',
name: 'PathRegex',
component: PathRegex,
pathToRegexpOptions: {
sensitive: true,
strict: true
}
},
{
path: '/hellokitty2',
redirect: '/hellokitty'
},
{
path: '/hellokitty3',
redirect: { name: 'HelloKitty' }
},
{
path: '*?',
name: 'NotFound',
component: NotFound
}
]
});
以上是大部分使用上的例子,不過由於 pathToRegexpOptions 比較特別,這裡就不多做解釋。
path 當中,你可以使用 * 來做萬用匹配。path 當中使用 :id 表示接受一個變數為 id 的數值。props: true 的話,可以將剛剛的 id 傳入元件中。:id 也可以加入正規,例如說 :id([0-9]+) 這樣的作法。redirect 就是轉頁的概念,他後面也可以接函式。alias 的概念就是設定好的路徑,會被導向同一組路由設定。beforeEnter 要記得呼叫 next() 他才會繼續往下做。children 的路徑就會接續他老爸再繼續往後,記得不要在 path 加 /,不然他會回到根目錄去。components 建議要有一個預設值 default,不然你的樣版內,非命名規則的樣版會無法顯示。另外一點,最上層的 Route 的開頭就一定要有 / 的設定,不然會被警告,且會失效!
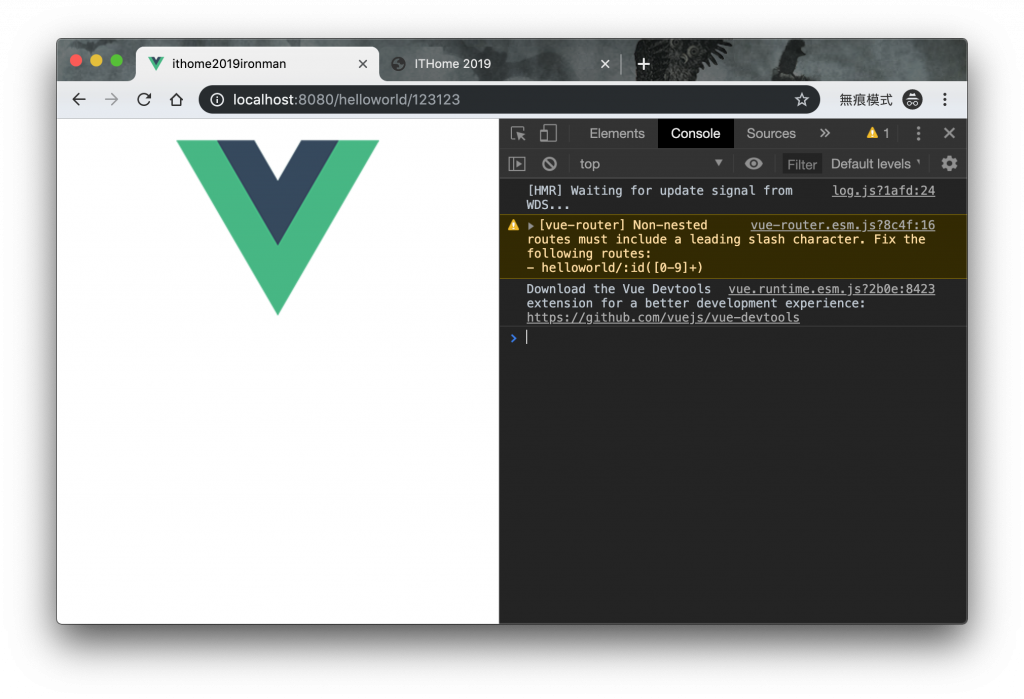
每個路由元件的載入,扣除最根元件以外,路由需要搭配一組元件來做應用。而在 App.vue 裡面,需要使用 <router-view> 來當作一個 Route 的進入點。而,若是你使用嵌套路由,那麼你的嵌套路由父元件也是需要一組 <router-view> 來作為進入點。
<template>
<section>
<router-view></router-view>
</section>
</template>
然而,<router-view> 有一個屬性 name 可以用,他的應用範圍,是將 Route 設定當中,有命名的元件來套用。在你的 Route 設定中,要使用 components 來設定,舉例來說,
<template>
<section>
<!-- 這個區段會渲染 `default` 的元件 -->
<router-view></router-view>
<!-- 這個區段會渲染命名為 `a` 的元件 -->
<router-view name="a"></router-view>
</section>
</template>
那麼你的路由設定可能是這樣,
import Router from 'vue-router'
import HelloKitty from '@/components/HelloKitty.vue'
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'HelloWorld',
components: {
default: HelloKitty,
a: HelloWorld
}
}
]
});
若是使用嵌套路由的話,就如同上述例子一樣,你必須提供一個 <router-view> 來當作進入點。
我們有了進入點之後,Vue Router 提供了一個樣版方法 <router-link> 用來渲染出對應的連結,這個樣版方法可以接受下列屬性:
to 接受命名的路由名稱,或是路由物件。路由物件包含了:
path 直接填寫路徑,不要與 name 混用。name 填入命名的路由名稱,不要與 path 混用。params 路由若有使用正規,則可填入路由正規所指定的變數數值,使用 Object 模式傳入。query 設定網址搜尋資料,亦即 ? 後面的設定值,使用 Object 模式傳入。replace 原本的 to 指令預設是使用 router.push() 的方式,若加了這個屬性,則會適用 router.replace() 的方式執行。若使用 replace,則你的 History 不會留下記錄。append 意思就是把現在的路徑 加入 這個 <router-link> 所設定的路徑。tag 原本 <router-link> 預設使用 A 標籤,這個設定可以讓你指定其他標籤。active-class 當路由正規規則符合時,會套用這個屬性所指定的類別名稱。預設會使用 router-link-active 這個名稱。exact 如果加入這個屬性,則需要正規 完全符合 的時候,才會套用 exact-active-class 指定的類別名稱。exact-active-class 當路由正規規則 完全符合 時,會套用這個屬性所指定的類別名稱。預設會使用 router-link-exact-active 這個名稱。event 觸發該路由的事件,預設是使用 click 事件。關於上述的 params,所謂路由正規其實就是文章上面範例中,所提到的 id/:id 這樣的例子,而這個例子在 <router-link> 當中的設定,看起來就會像這個樣子:
<template>
<section>
<router-link
:to="{ name: 'HelloKittyWithId', params: { id: 123 } }"
></router-link>
</section>
</template>
而在 Vue Router 3.1.0 版本之後,對於 <router-link> 則提供了一個插槽( Slot )的新功能。這個功能可以讓你替換調原本 <router-link> 的結構,這個插槽提供了幾個數值讓你使用:
href 解析過後的網址,提供給 A 標籤的 href 使用的字串。route 傳回一個 Route 的完整物件。navigate 觸發路由的事件函式, 必要時會阻止此事件執行 。isActive 回傳路由正規是否符合,回傳值為布林值。isExactActive 回傳路由正規是否 完全符合 ,回傳值為布林值。這個新功能可以讓你自己決定你的 <router-link> 會長成什麼樣子。舉例來說:
<template>
<section>
<router-link
v-slot="{ href, route, navigate, isActive, isExactActive }"
>
<a :href="href" @click="navigate">
<img src="./assets/img/logo.png" alt="Logo">
<span>{{ route.fullPath }}</span>
</a>
</router-link>
</section>
</template>
請注意,若你的 A 標籤有使用
target="_blank",則navigate會被忽略。
另外有一件事情,由於 <router-link> 實際上只是幫你做路由的動作,所以,如果你在 <router-link> 上面綁定了 click 的時候,你會發現沒有被觸發:
<template>
<section>
<router-link to="hello" @click="hello">Hello</router-link>
<router-link to="kitty" @click.native="kitty">Kitty</router-link>
</section>
</template>
上述的例子,只有 kitty 這個事件會被觸發。亦即,你必須要在 click 事件的後方,加入 .native 修飾子才會有效。有沒有加入 .native 的差異在於,一般在 Vue 的事件綁定中,是以 Vue-Event 為主,而加上了 .native 則代表,你想要觸發的是 DOM 的原生事件。
是的,在 <router-link> 這個元件上,需要用到 .native 來確保事件發生。不然,<router-link> 基本上都會直接忽略你所綁定的事件。
前端路由確實是一個風潮,只是說不知道能持續多久?倘若以 SPA 來看,大家都做成一頁了,好像也沒必要使用前端路由了?
但是,
你覺得我會這麼安分的就這樣放過路由這件事嗎?
剩下的,就待下回分曉了(燦笑)。
